RELATIONAL DATABASE FUNDAMENTALS
- Database - maintains information about various types of objects (inventory), events (transactions), people (employees) and places (warehouses)
Database models include :
- Hierarchical database model - information is organized into tree-like structure (using parent/child relationships) in such a way that it cannot have too many relationships.

2. Network database model - a flexible way of representing objects and their relationships.

3. Relational database model - stores information in the form of logically related two- dimensional tables.
Entities and Attributes
Entity - a person, place, thing, transaction or event about which information is stored.
Attributes (fields, columns) - characteristics or properties of an entity class.
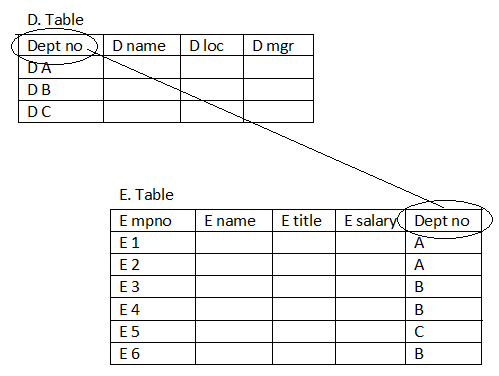
Keys and Relationships
Primary key - a field (or group of fields) that uniquely identities a given entity in a table.
Foreign key - a primary key of one table that appears an attribute in another table and acts to provide a logical relationship among the two tables.
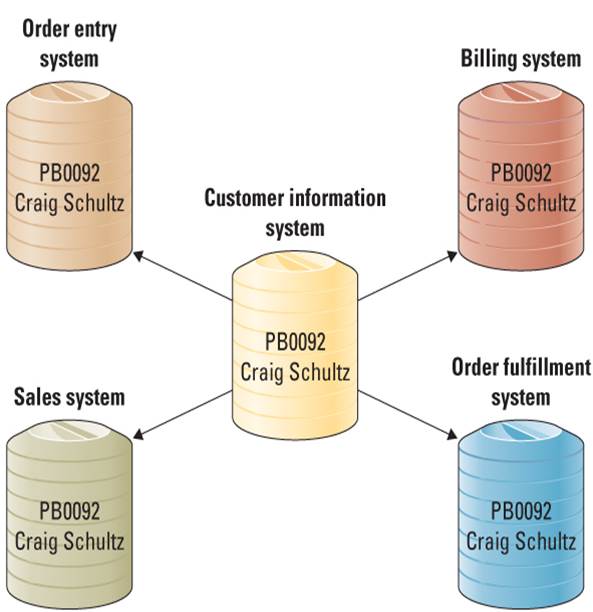
Integrating Information Among Multiple Database
Building a central repository specifically for integrated information.
RELATIONAL DATABASE ADVANTAGES
1) Increased Flexibility
- Database provide flexibility in allowing each user to access the information in whatever way best suits his or her needs.
- The distinction between logical and physical views is important in understanding flexible database user views.
-The physical views of information deals with the physical storage of information on a storage device such as a hard disk.
- The logical views of information focuses on how users logically access information to meet their particular business.
2) Increased Scalability and Performance
-
Only a database could 'scale' to handle the massive volumes of
information and the large numbers of users required for the successful
launch of the Ellis Island website.
- Scalability refers to how well a system can adapt to increased demand.
- Performance measures how quickly a system performs a certain process or transaction.
3) Reduced Information Redundancy
- Redundancy is the duplication of information, or storing the same information in multiple places.
- Redundant information occurs because organizations frequently capture and store the same information in multiple locations.
- The primary problem with
redundant information is that it is often inconsistent which make it
difficult to determine which values are the most current or most
accurate.
4) Increased Information Integrity (Quality)
- Information integrity is a measures the quality of information
- Within a database environment, integrity constraints are rules that help ensure the quality of information. It can be defined and built into the database design.
- Two types of integrity constraints are :
- Relational integrity constraints- rules that enforce basic and fundamental information-based constraints
- Business-critical integrity constraints- enforce business rules vital to an organization's success and often require more insight and knowledge than relational integrity constraints.
5) Increased Information Security
- Information is an organizational asset.
- Database offer many security features such as
* Passwords - provide authentication of the user
* Access levels - determines who has access to the different types of information
* Access control -
determines types of user access such as customer service
representatives might
read-only access
- Database can increase personal security as well as information security
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
A database management systems (DBMS) is software through which users and application programs interact with a database.
DATA-DRIVEN WEB SITES
- A data-driven website is an
interactive website keep constantly updated and relevant to the needs of
its costumer through the use of a database.
Data-Driven Website Advantages :-
- Development : Allows the website owner to make changes any time
- Content management : A static website requires a programmer to make updates.
- Future expandability : Having a data-driven website enables the site to grow faster than would be possible with a static site.
- Minimizing human error : A well- designed, data-driven Web site will have "error typing" mechanisms to ensure that required information is filled out correctly.
- Cutting production and update costs : A data-driven Web site can be updated and "published" by any competent data entry or administrative person.
- More efficient : The system keeps track of the templates.
- Improved stability : There is peace of mind, knowing the content is never lost-even if your programmer is.
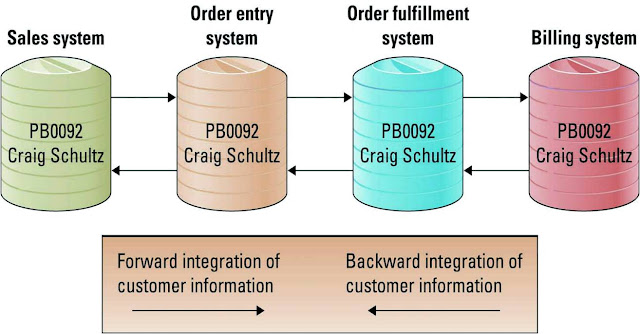
- An integration allows separate systems to communicate directly with each other.
- A forward integration takes information entered into a given system and sends it automatically to all downstream processes. This type of integration always use by the organization.
- A backward integration - takes information entered into a given systems and sends it automatically to all upstream systems and processes

Building a central repository specifically for integrated information.

Without the integration, an organization will :
- spend considerable time entering the same info in multiple system
- suffer from the low quality and inconsistency typically embedded in redundant info.

































